
Understanding the five s’s of lean manufacturing is essential if you want to transform your manufacturing processes into a lean machine. They are Standardize, Straighten, Shine, and Sustain. These are the steps to follow. Your lean transformation will be maximized if you train your frontline employees and team leaders.
Standardize
Clean up and organize your workspace as the first step in the 5S Process. This may be a one-time job, but if you standardize the process, it can become a routine. You can use checklists, visual cues, and checklist templates to create a consistent approach to 5S tasks.
These five s's can help your workplace be more productive and efficient. This approach will encourage your staff to be organized and do their jobs in a streamlined manner. This will help improve your efficiency by organizing your work area. These five s’s are helpful for improving safety in the workplace. An organized workspace can prevent accidents and reduce the chances of making mistakes. It will also increase productivity.
Straighten
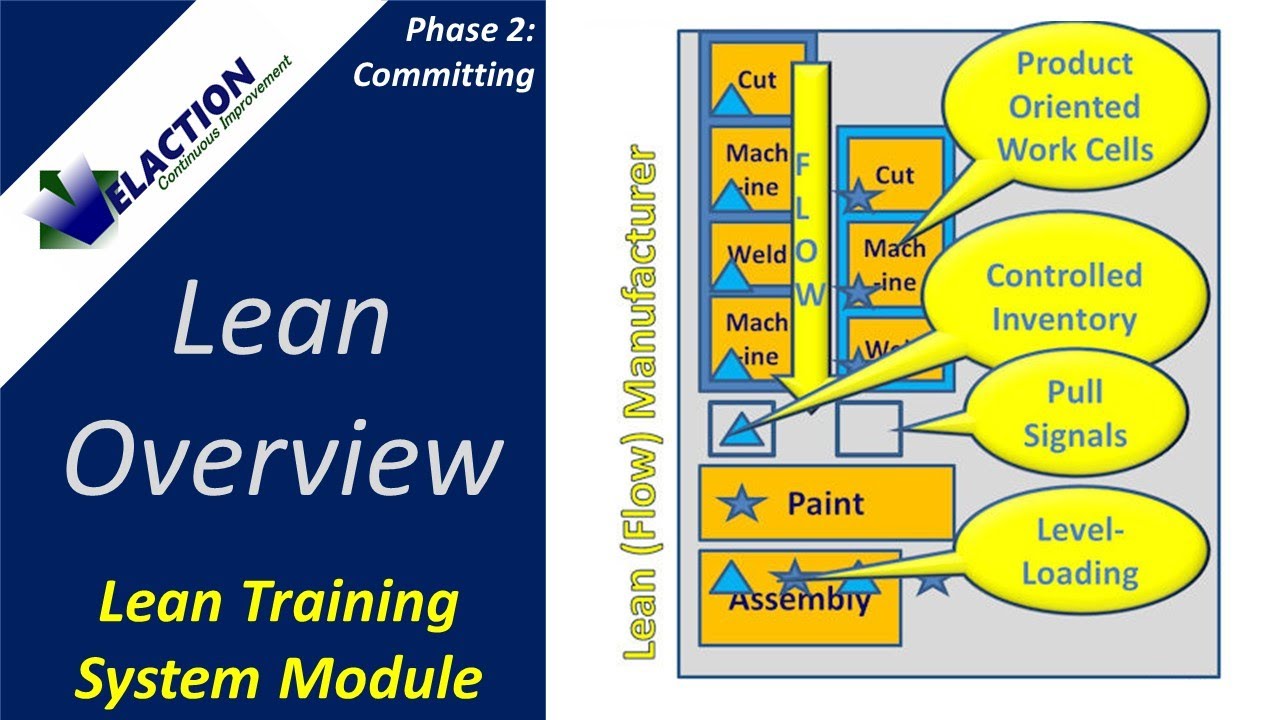
Straightening your 5 s's of lean doesn't have to be difficult. Companies can improve their business processes by applying lean principles in a systematic way. For example, by organizing the components of an assembly line, workers will be able to find the components they need more easily. This can reduce the amount of time spent looking for misplaced parts, and improve workflow efficiency and company safety.
Reducing the number and type of items in each workspace will help you save money. This can help you reduce your office supply bills. Straightening the work cells can save you money and improve productivity.
Shine
Shine focuses on the inspection of the workspace and identifying any potential problems. By examining equipment and tools, Shine helps to improve flow and reduce waste. Shine makes it easier to maintain a workspace. It helps increase output by standardizing the layout of a workspace.
Shine is a tool that can be used to lean manufacturing. This technique automates work, reducing waste and increasing efficiency. It can also be used in manufacturing. This applies the 5S principles throughout a company. It reduces inventory, work in progress, and supplies stock.
Sustain
In order to sustain the 5 s’s of lean, you need to bring back a standardized system into a facility. This is a process that is meant to be continuous and should be repeated often to ensure the facility works at its best. Employees should be trained to conduct 5S audits.
The 5S method emphasizes reducing waste, increasing productivity, and maintaining an orderly work environment. It is basically a way to organize workplaces according to the five principles of Toyota Production System. Hiroyuki Hirano created it post-war Japan to improve manufacturing efficiency.
FAQ
Why is logistics important for manufacturing?
Logistics are an integral part any business. Logistics can help you achieve amazing results by helping to manage product flow from raw materials to finished products.
Logistics are also important in reducing costs and improving efficiency.
What kind of jobs are there in logistics?
Logistics can offer many different jobs. Some of them are:
-
Warehouse workers - They load trucks and pallets.
-
Transportation drivers – These drivers drive trucks and wagons to transport goods and pick up the goods.
-
Freight handlers - They sort and pack freight in warehouses.
-
Inventory managers - They oversee the inventory of goods in warehouses.
-
Sales reps - They sell products and services to customers.
-
Logistics coordinators - They plan and organize logistics operations.
-
Purchasing agents - They purchase goods and services needed for company operations.
-
Customer service representatives - Answer calls and email from customers.
-
Shipping clerks - They process shipping orders and issue bills.
-
Order fillers: They fill orders based off what has been ordered and shipped.
-
Quality control inspectors – They inspect incoming and outgoing products to ensure that there are no defects.
-
Other - Logistics has many other job opportunities, including transportation supervisors, logistics specialists, and cargo specialists.
How can I learn about manufacturing?
Hands-on experience is the best way to learn more about manufacturing. However, if that's not possible, you can always read books or watch educational videos.
Can we automate some parts of manufacturing?
Yes! Automation has been around since ancient times. The Egyptians discovered the wheel thousands and years ago. To help us build assembly lines, we now have robots.
In fact, there are several applications of robotics in manufacturing today. These include:
-
Line robots
-
Robot welding
-
Robot painting
-
Robotics inspection
-
Robots create products
Automation could also be used to improve manufacturing. For example, 3D printing allows us to make custom products without having to wait for weeks or months to get them manufactured.
What is the job of a production plan?
Production planners make sure that every aspect of the project is delivered on-time, within budget, and within schedule. A production planner ensures that the service and product meet the client's expectations.
Why automate your warehouse
Modern warehouses have become more dependent on automation. The rise of e-commerce has led to increased demand for faster delivery times and more efficient processes.
Warehouses need to adapt quickly to meet changing needs. Technology investment is necessary to enable warehouses to respond quickly to changing demands. Automation of warehouses offers many benefits. Here are some reasons why it's worth investing in automation:
-
Increases throughput/productivity
-
Reduces errors
-
Improves accuracy
-
Safety Boosts
-
Eliminates bottlenecks
-
Companies can scale up more easily
-
Makes workers more efficient
-
It gives visibility to everything that happens inside the warehouse
-
Enhances customer experience
-
Improves employee satisfaction
-
Reducing downtime and increasing uptime
-
Quality products delivered on time
-
Eliminates human error
-
It ensures compliance with regulations
What is the difference between Production Planning, Scheduling and Production Planning?
Production Planning (PP) refers to the process of determining how much production is needed at any given moment. Forecasting demand is one way to do this.
Scheduling is the process of assigning specific dates to tasks so they can be completed within the specified timeframe.
Statistics
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
Six Sigma in Manufacturing:
Six Sigma is defined by "the application SPC (statistical process control) techniques to achieve continuous improvements." It was developed by Motorola's Quality Improvement Department at their plant in Tokyo, Japan, in 1986. Six Sigma is a method to improve quality through standardization and elimination of defects. Many companies have adopted this method in recent years. They believe there is no such thing a perfect product or service. The main goal of Six Sigma is to reduce variation from the mean value of production. If you take a sample and compare it with the average, you will be able to determine how much of the production process is different from the norm. If it is too large, it means that there are problems.
Understanding the dynamics of variability within your business is the first step in Six Sigma. Once you have this understanding, you will need to identify sources and causes of variation. These variations can also be classified as random or systematic. Random variations happen when people make errors; systematic variations are caused externally. For example, if you're making widgets, and some of them fall off the assembly line, those would be considered random variations. But if you notice that every widget you make falls apart at the exact same place each time, this would indicate that there is a problem.
After identifying the problem areas, you will need to devise solutions. It might mean changing the way you do business or redesigning it entirely. To verify that the changes have worked, you need to test them again. If they fail, you can go back to the drawing board to come up with a different plan.