
Companies can ensure products are created in a way that meets their needs using lean product-development methodologies. They are able to reduce waste, speed up product development and ensure that products meet customers' needs. Companies can remain competitive through the use of lean processes.
Lean product development is an approach that integrates engineering work with manufacturing work. Its purpose, is to produce a working product using less time, stock and effort. It includes rapid learning cycles and uses visual planning techniques such as visual boards. It also incorporates set-based concurrent Engineering.
Lean product development begins with understanding the customer. This involves understanding the customer and identifying the risks involved in the business plan. It is important that you understand the product's functionality and features. These features are often unnecessary and excessive if the customer does not require them. This includes the creation of a verification plan and validation plan.
Next, we need to build an activity network. This allows teams the freedom to decide what they do and how they plan it. This network allows teams to develop their own value. It reduces waste and assists teams in finding ways to improve their processes.
The ideal PD process is focused on a continuous flow in value from conception to production. It should be free of bureaucratic repercussions and loopbacks that correct errors. It should be able to represent the entire value stream. The system should not be broken down or lead to systemic vision loss. This process should also work like a single piece flow in manufacturing.
The first step is to determine its value. This is done through an analysis of the business case and a systematic literature review. It is essential that all stakeholders agree on the expectations regarding value. It is important to define the product scope. This includes customer value as well as the features and functions. These elements will determine the technology and the process.
The next step is to create the value stream. This is done by identifying and eliminating steps in the value stream that don't add value. Unused designs and unverified codes should be eliminated. It is important to reduce the number and complexity of tasks that are being performed simultaneously. This is usually done through frequent changes in priorities.
Lean product design is a powerful tool that businesses can use to reduce costs, improve processes and stay competitive. Lean product development allows companies to create sustainable value streams that will allow them to be profitable in the future. It has been a great help to companies in every industry, including high-tech manufacturing and healthcare.
Lean product engineering uses a set based concurrent engineering approach which allows teams and individuals to develop products with fewer resources. It used to take longer for big companies to develop new products than it did for start-ups due to their complex codebases. This codebase can be hard to maintain and improve upon.
FAQ
What does warehouse refer to?
A warehouse, or storage facility, is where goods are stored prior to being sold. You can have it indoors or outdoors. It could be one or both.
What skills is required for a production planner?
Production planners must be flexible, organized, and able handle multiple tasks. Also, you must be able and willing to communicate with clients and coworkers.
Do we need to know about Manufacturing Processes before learning about Logistics?
No. You don't have to know about manufacturing processes before learning about logistics. Understanding the manufacturing process will allow you to better understand logistics.
Statistics
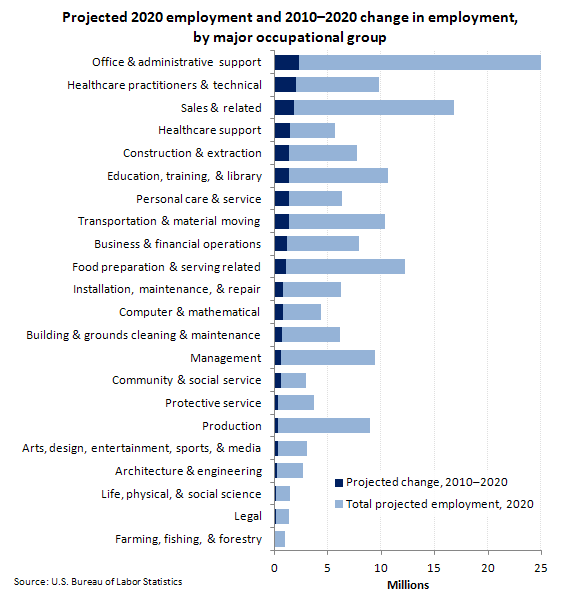
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
External Links
How To
How to Use Just-In-Time Production
Just-intime (JIT), a method used to lower costs and improve efficiency in business processes, is called just-in-time. It allows you to get the right amount resources at the right time. This means you only pay what you use. Frederick Taylor first coined this term while working in the early 1900s as a foreman. He observed how workers were paid overtime if there were delays in their work. He concluded that if workers were given enough time before they start work, productivity would increase.
JIT teaches you to plan ahead and prepare everything so you don’t waste time. You should also look at the entire project from start to finish and make sure that you have sufficient resources available to deal with any problems that arise during the course of your project. You can anticipate problems and have enough equipment and people available to fix them. This will ensure that you don't spend more money on things that aren't necessary.
There are many JIT methods.
-
Demand-driven JIT: This is a JIT that allows you to regularly order the parts/materials necessary for your project. This will allow to track how much material has been used up. It will also allow you to predict how long it takes to produce more.
-
Inventory-based: This allows you to store the materials necessary for your projects in advance. This allows for you to anticipate how much you can sell.
-
Project-driven: This is an approach where you set aside enough funds to cover the cost of your project. Knowing how much money you have available will help you purchase the correct amount of materials.
-
Resource-based JIT : This is probably the most popular type of JIT. You allocate resources based on the demand. You will, for example, assign more staff to deal with large orders. If you don’t have many orders you will assign less people to the work.
-
Cost-based: This approach is very similar to resource-based. However, you don't just care about the number of people you have; you also need to consider how much each person will cost.
-
Price-based: This approach is very similar to the cost-based method except that you don't look at individual workers costs but the total cost of the company.
-
Material-based - This is a variant of cost-based. But instead of looking at the total company cost, you focus on how much raw material you spend per year.
-
Time-based JIT: A variation on resource-based JIT. Instead of worrying about how much each worker costs, you can focus on how long the project takes.
-
Quality-based JIT is another variant of resource-based JIT. Instead of thinking about the cost of each employee or the time it takes to produce something, you focus on how good your product quality.
-
Value-based JIT: One of the most recent forms of JIT. In this case, you're not concerned with how well the products perform or whether they meet customer expectations. Instead, you are focused on adding value to the marketplace.
-
Stock-based: This stock-based method focuses on the actual quantity of products being made at any given time. This method is useful when you want to increase production while decreasing inventory.
-
Just-in-time (JIT) planning: This is a combination of JIT and supply chain management. It is the process of scheduling components' delivery as soon as they have been ordered. This is important as it reduces lead time and increases throughput.