The Industrial Products & Services sector of the industrial manufacturing industry is experiencing increased global competition and a shortage in skilled workers. The 2020s will present a challenging environment for the industrial manufacturing market. To optimize growth in established markets as well as to identify growth opportunities, the Industrial Products & Services market requires a holistic culture of Innovation.
According to Deloitte and Manufacturing Institute, the US manufacturing sector will be experiencing the greatest shortage in skilled workers since the beginning of history. This is because 2 million jobs are unfilled over the next ten-years. As the industry prepares to face the future, manufacturers will need to decide how they will innovate and develop their digital capabilities. Deloitte's Industrial Manufacturing team can assist manufacturers in navigating the industry landscape.
As the fourth industrial revolution continues to disrupt the manufacturing sector, the industry must prepare the workforce for a future that will involve networking within the 'internet of things' and digital transformation. The Industrial Manufacturing team is experienced in establishing innovation management models that are grounded in industry-specific expertise and deep knowledge of the industry. It also provides a wide range of digital transformation services that can help manufacturers to thrive in a world of digital disruption.
The Deloitte report is based on extensive secondary information analysis of labor supply. Interviews with executives from various manufacturing companies are also part of the research. Economic projections are also included. These findings highlight the importance and value of having a diverse workforce. Half of respondents identified adaptability to company values being a key aspect of their job satisfaction. In addition, more than one-third of respondents reported that they believe employees need to have a purpose in order to feel satisfied at work. Executives also think that millennials value environmental awareness and are increasingly interested in climate change issues.
Deloitte's Oxford Economic Model predicts that the manufacturing GDP will rise at a moderate pace of 1.3 per cent in 2020. The study points out that this growth rate is less than half the rate experienced in recent years. This will force companies to rethink their supply chain assurance strategies. In addition, companies will need to focus on broader management initiatives such as increasing resilience in operations. In fact, the Deloitte study indicates that manufacturers will likely be making decisions about workplaces and work practices.
Manufacturing companies need to create career pathways and build an inclusive culture to ensure they are ready for the future. It is possible to improve manufacturing efficiency by increasing resilience and reduce waste. Combining digital technologies with lean principles can help to reduce manufacturing variability.
Deloitte released a new report on diversity in manufacturing as the US manufacturing industry continues its evolution. Deloitte's "Beyond Reskilling" report discusses how diversity is essential to manufacturing's future, and it highlights the benefits of having a diverse workforce.
FAQ
Why automate your factory?
Modern warehouses have become more dependent on automation. E-commerce has increased the demand for quicker delivery times and more efficient processes.
Warehouses need to adapt quickly to meet changing needs. To do so, they must invest heavily in technology. The benefits of automating warehouses are numerous. These are some of the benefits that automation can bring to warehouses:
-
Increases throughput/productivity
-
Reduces errors
-
Increases accuracy
-
Safety enhancements
-
Eliminates bottlenecks
-
Allows companies to scale more easily
-
Workers are more productive
-
Gives you visibility into all that is happening in your warehouse
-
Enhances customer experience
-
Improves employee satisfaction
-
It reduces downtime, and increases uptime
-
You can be sure that high-quality products will arrive on time
-
Human error can be eliminated
-
It helps ensure compliance with regulations
What's the difference between Production Planning & Scheduling?
Production Planning (PP) refers to the process of determining how much production is needed at any given moment. This is done through forecasting demand and identifying production capacities.
Scheduling refers the process by which tasks are assigned dates so that they can all be completed within the given timeframe.
What is the role and responsibility of a Production Planner?
Production planners ensure all aspects of the project are delivered within time and budget. A production planner ensures that the service and product meet the client's expectations.
What is the importance of automation in manufacturing?
Not only are service providers and manufacturers important, but so is automation. It allows them provide faster and more efficient services. In addition, it helps them reduce costs by reducing human errors and improving productivity.
How does a production planner differ from a project manager?
A production planner is more involved in the planning phase of the project than a project manger.
What does it take to run a logistics business?
To run a successful logistics company, you need a lot knowledge and skills. For clients and suppliers to be successful, you need to have excellent communication skills. You must be able analyze data and draw out conclusions. You must be able manage stress and pressure under pressure. To increase efficiency and creativity, you need to be creative. To motivate and guide your team towards reaching organizational goals, you must have strong leadership skills.
You should also be organized and efficient to meet tight deadlines.
What is the difference between manufacturing and logistics
Manufacturing is the production of goods using raw materials. Logistics is the management of all aspects of supply chain activities, including procurement, production planning, distribution, warehousing, inventory control, transportation, and customer service. As a broad term, manufacturing and logistics often refer to both the creation and delivery of products.
Statistics
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
External Links
How To
How to use Lean Manufacturing in the production of goods
Lean manufacturing (or lean manufacturing) is a style of management that aims to increase efficiency, reduce waste and improve performance through continuous improvement. It was developed in Japan between 1970 and 1980 by Taiichi Ohno. TPS founder Kanji Tyoda gave him the Toyota Production System, or TPS award. The first book published on lean manufacturing was titled "The Machine That Changed the World" written by Michael L. Watkins and published in 1990.
Lean manufacturing, often described as a set and practice of principles, is aimed at improving the quality, speed, cost, and efficiency of products, services, and other activities. It emphasizes eliminating waste and defects throughout the value stream. Just-in-time (JIT), zero defect (TPM), and 5S are all examples of lean manufacturing. Lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating non-value-added activities such as rework, inspection, and waiting.
Lean manufacturing is a way for companies to achieve their goals faster, improve product quality, and lower costs. Lean Manufacturing is one of the most efficient ways to manage the entire value chains, including suppliers and customers as well distributors and retailers. Lean manufacturing practices are widespread in many industries. For example, Toyota's philosophy underpins its success in automobiles, electronics, appliances, healthcare, chemical engineering, aerospace, paper, food, etc.
Lean manufacturing includes five basic principles:
-
Define Value: Identify the social value of your business and what sets you apart.
-
Reduce waste - Stop any activity that isn't adding value to the supply chains.
-
Create Flow - Ensure work moves smoothly through the process without interruption.
-
Standardize and simplify – Make processes as repeatable and consistent as possible.
-
Building Relationships – Establish personal relationships with both external and internal stakeholders.
Although lean manufacturing isn't a new concept in business, it has gained popularity due to renewed interest in the economy after the 2008 global financial crisis. Many businesses have adopted lean manufacturing techniques to help them become more competitive. Many economists believe lean manufacturing will play a major role in economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing has many benefits in the automotive sector. These include improved customer satisfaction, reduced inventory levels, lower operating costs, increased productivity, and better overall safety.
You can apply Lean Manufacturing to virtually any aspect of your organization. Lean manufacturing is most useful in the production sector of an organisation because it ensures that each step in the value-chain is efficient and productive.
There are three types of lean manufacturing.
-
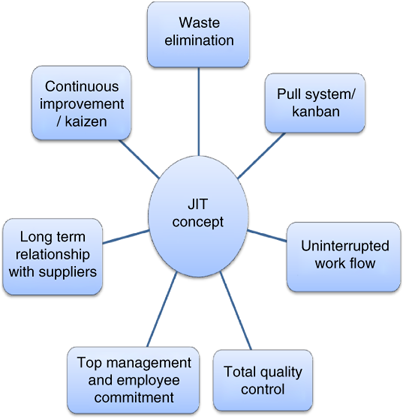
Just-in Time Manufacturing, (JIT): This kind of lean manufacturing is also commonly known as "pull-systems." JIT is a process in which components can be assembled at the point they are needed, instead of being made ahead of time. This approach aims to reduce lead times, increase the availability of parts, and reduce inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing, (ZDM): ZDM is focused on ensuring that no defective products leave the manufacturing facility. You should repair any part that needs to be repaired during an assembly line. This is true even for finished products that only require minor repairs prior to shipping.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI),: Continuous improvement aims improve the efficiency and effectiveness of operations by continuously identifying issues and making changes to reduce waste. Continuous Improvement (CI) involves continuous improvement in processes, people, tools, and infrastructure.