
In classical economics, there are three basic sectors. These categories include manufacturing, services, as well as financial activities. Businesses are classified based on their characteristics and risk. You will find out more about each sector below. This is a brief overview of the types of businesses in each sector. This information can be further explored if you are curious. You should remember that these categories can't be considered mutually exclusive.
Economic activity
Factors that are used to produce, inputs, or outputs affect the country's economic activity. A region's ability to produce a particular product or service determines its economic activity. There are two types of economic activity: primary and secondary. Primary economic activities produce goods and services that satisfy human needs. While secondary economic activities add value by combining raw materials into a better product, they are not as valuable. Some examples of secondary economic activities include manufacturing and processing industries.
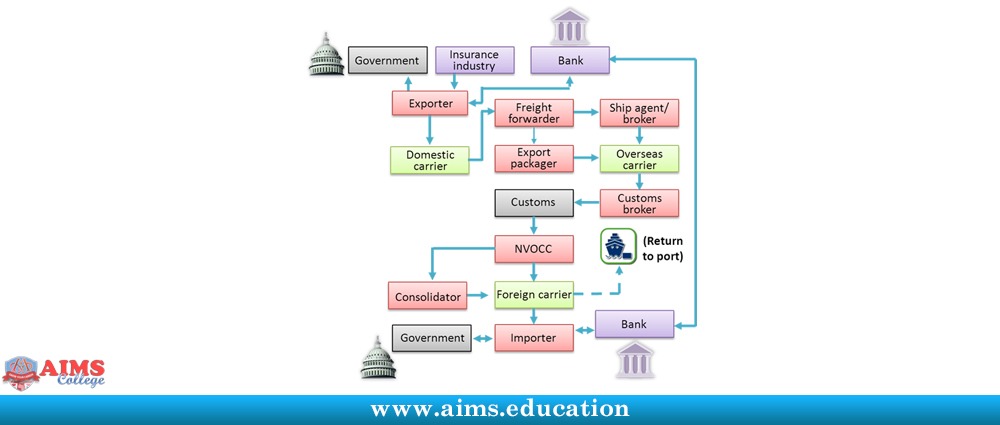
Classification
Business classification refers the process of dividing businesses in groups based their type of activities. There are two main categories: primary and secondary. Primary businesses are those which extract or exchange natural resources. The second kind of business converts raw materials and produces products for sale. There are many distinctions between these two types. Listed below are some of the major differences between the two types. The information in this article will help you to decide which type is right for your business.
Characteristics
The following discussion discusses the differences between the primary and secondary sectors. It also focuses on the impact each sector has on the economy. First, let's define sectors. Sectors are distinct economic entities that react differently to different factors. These situations may arise from repeated events such as business cycles or single events such as technological advances. These characteristics can be useful for identifying the most promising sectors and determining their relative importance in an economic economy.
There are always risks
Industry risk is the variation in performance across industries and their companies. It can be measured through assessing variances in profitability (ROE) or return on equity. Depending on the industry, this may also reflect the performance of stock markets. For example, a company that manufactures steel is considered to be high risk because of the potential for a major earthquake in the region. A study of such risks may help investors determine which sectors are more volatile.
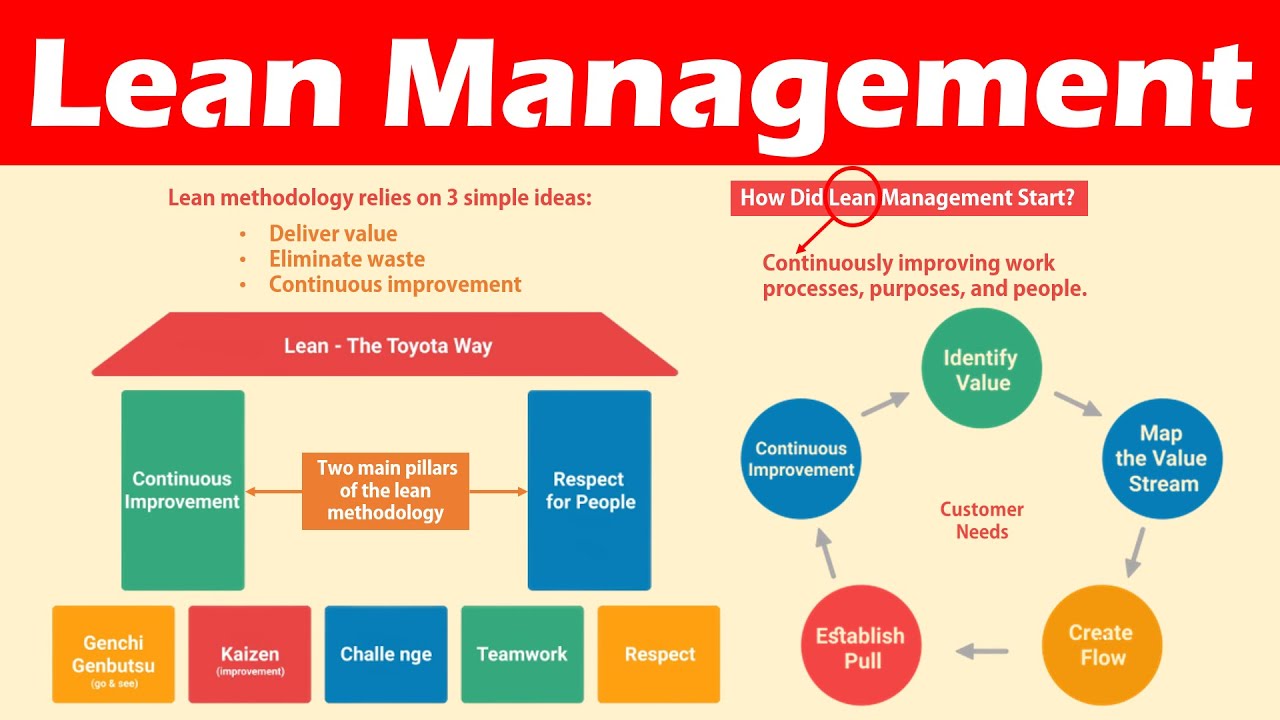
Investments
While some investors may invest in specific companies or sectors, others might choose to invest in broader areas. Sectors offer lower risks and can be found in mutual funds and exchange-traded funds. Sector investing is also becoming a popular investment strategy. This article will help you identify the best investments. For more information, please read on. For more information, don't miss our free resource section.
FAQ
What are the essential elements of running a logistics firm?
You need to have a lot of knowledge and skills to manage a successful logistic business. Effective communication skills are necessary to work with suppliers and clients. You should be able analyse data and draw inferences. You need to be able work under pressure and manage stressful situations. You need to be innovative and creative to come up with new ways to increase efficiency. You need to have strong leadership qualities to motivate team members and direct them towards achieving organizational goals.
It is also important to be efficient and well organized in order meet deadlines.
Why automate your warehouse
Modern warehousing is becoming more automated. E-commerce has brought increased demand for more efficient and quicker delivery times.
Warehouses should be able adapt quickly to new needs. To do so, they must invest heavily in technology. Automation of warehouses offers many benefits. These are just a few reasons to invest in automation.
-
Increases throughput/productivity
-
Reduces errors
-
Increases accuracy
-
Safety Boosts
-
Eliminates bottlenecks
-
Companies can scale more easily
-
This makes workers more productive
-
This gives you visibility into what happens in the warehouse
-
Enhances customer experience
-
Improves employee satisfaction
-
Reduces downtime and improves uptime
-
High quality products delivered on-time
-
Human error can be eliminated
-
It helps ensure compliance with regulations
What is the difference between Production Planning and Scheduling?
Production Planning (PP), also known as forecasting and identifying production capacities, is the process that determines what product needs to be produced at any particular time. This is done through forecasting demand and identifying production capacities.
Scheduling is the process of assigning specific dates to tasks so they can be completed within the specified timeframe.
What is manufacturing and logistics?
Manufacturing is the production of goods using raw materials. Logistics manages all aspects of the supply chain, including procurement, production planning and distribution, inventory control, transportation, customer service, and transport. Sometimes manufacturing and logistics are combined to refer to a wider term that includes both the process of creating products as well as their delivery to customers.
What is the role of a logistics manager
Logistics managers make sure all goods are delivered on schedule and without damage. This is done through his/her expertise and knowledge about the company's product range. He/she must also ensure sufficient stock to meet the demand.
Can we automate some parts of manufacturing?
Yes! Automation has been around since ancient times. The Egyptians created the wheel thousands years ago. Today, robots assist in the assembly of lines.
Actually, robotics can be used in manufacturing for many purposes. These include:
-
Automation line robots
-
Robot welding
-
Robot painting
-
Robotics inspection
-
Robots that produce products
Manufacturing can also be automated in many other ways. 3D printing, for example, allows us to create custom products without waiting for them to be made.
What jobs are available in logistics?
There are many kinds of jobs available within logistics. Here are some:
-
Warehouse workers: They load and unload trucks, pallets, and other cargo.
-
Transportation drivers – These drivers drive trucks and wagons to transport goods and pick up the goods.
-
Freight handlers are people who sort and pack freight into warehouses.
-
Inventory managers - These are responsible for overseeing the stock of goods in warehouses.
-
Sales reps are people who sell products to customers.
-
Logistics coordinators are responsible for organizing and planning logistics operations.
-
Purchasing agents are those who purchase goods and services for the company.
-
Customer service representatives - Answer calls and email from customers.
-
Shipping clerks – They process shipping orders, and issue bills.
-
Order fillers - They fill orders based on what is ordered and shipped.
-
Quality control inspectors are responsible for inspecting incoming and outgoing products looking for defects.
-
Others - There are many types of jobs in logistics such as transport supervisors and cargo specialists.
Statistics
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
How to Use Just-In-Time Production
Just-in-time is a way to cut costs and increase efficiency in business processes. It is a process where you get the right amount of resources at the right moment when they are needed. This means that you only pay for what you actually use. Frederick Taylor developed the concept while working as foreman in early 1900s. He observed how workers were paid overtime if there were delays in their work. He decided that workers would be more productive if they had enough time to complete their work before they started to work.
JIT is an acronym that means you need to plan ahead so you don’t waste your money. Look at your entire project, from start to end. Make sure you have enough resources in place to deal with any unexpected problems. If you expect problems to arise, you will be able to provide the necessary equipment and personnel to address them. This way, you won't end up paying extra money for things that weren't really necessary.
There are many JIT methods.
-
Demand-driven: This type of JIT allows you to order the parts/materials required for your project on a regular basis. This will enable you to keep track of how much material is left after you use it. This will let you know how long it will be to produce more.
-
Inventory-based: This type allows you to stock the materials needed for your projects ahead of time. This allows you predict the amount you can expect to sell.
-
Project-driven : This is a method where you make sure that enough money is set aside to pay the project's cost. You will be able to purchase the right amount of materials if you know what you need.
-
Resource-based JIT is the most widespread form. Here, you allocate certain resources based on demand. If you have many orders, you will assign more people to manage them. If you don't receive many orders, then you'll assign fewer employees to handle the load.
-
Cost-based: This is the same as resource-based except that you don't care how many people there are but how much each one of them costs.
-
Price-based: This approach is very similar to the cost-based method except that you don't look at individual workers costs but the total cost of the company.
-
Material-based - This is a variant of cost-based. But instead of looking at the total company cost, you focus on how much raw material you spend per year.
-
Time-based: This is another variation of resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing solely on the amount each employee costs, focus on how long it takes for the project to be completed.
-
Quality-based JIT - This is another form of resource-based JIT. Instead of thinking about how much each employee costs or how long it takes to manufacture something, you think about how good the quality of your product is.
-
Value-based JIT: One of the most recent forms of JIT. In this instance, you are not concerned about the product's performance or meeting customer expectations. Instead, you focus on the added value that you provide to your market.
-
Stock-based: This inventory-based approach focuses on how many items are being produced at any one time. This method is useful when you want to increase production while decreasing inventory.
-
Just-intime planning (JIT), is a combination JIT/sales chain management. This refers to the scheduling of the delivery of components as soon after they are ordered. It reduces lead times and improves throughput.